.NET Native AOT support
Excel-DNA can produce native 64-bit Excel add-ins, that can run on machines that don't have the .NET runtime installed, using .NET 8.0 (or later) Native AOT deployment and ExcelDna.AddIn.NativeAOT package.
Notes for .NET 10 / preview package users
When using early preview package sets (from NuGet.org or another trusted feed), keep these points in mind:
- Align all
ExcelDna.*package versions acrossExcelDna.AddIn,ExcelDna.Integration, andExcelDna.AddIn.NativeAOTso they come from the same preview train. - The generated build output for NativeAOT variants is typically under a RID-specific path (for example
bin\\<Config>\\<TFM>\\win-x64\\...) rather than the managed default output path. - In preview or custom source setups, if you see a build error like
File does not exist (Xll32FilePath): ... ExcelDna.xll, you can explicitly pointExcelDnaToolsPathat theExcelDna.AddInpackage tools folder:
<PropertyGroup>
<ExcelDnaToolsPath>$(PkgExcelDna_AddIn)\\tools\\</ExcelDnaToolsPath>
</PropertyGroup>
Publishing the following MyAddin.csproj C# project produces native 64-bit MyAddin-AddIn64.xll Excel add-in:
<Project Sdk="Microsoft.NET.Sdk">
<PropertyGroup>
<TargetFramework>net10.0-windows</TargetFramework>
<ImplicitUsings>enable</ImplicitUsings>
<Nullable>enable</Nullable>
<RuntimeIdentifier>win-x64</RuntimeIdentifier>
<PublishAOT>true</PublishAOT>
</PropertyGroup>
<ItemGroup>
<PackageReference Include="ExcelDna.AddIn.NativeAOT" Version="1.10.0-preview1" />
</ItemGroup>
</Project>
Supported functionality in native add-ins
Function
internal class Functions
{
[ExcelFunction]
public static string NativeHello(string name)
{
return $"Hello {name}!";
}
[ExcelFunction]
public static int NativeSum(int i1, int i2)
{
return i1 + i2;
}
}
| Cell | Formula | Result |
|---|---|---|
| A1 | =NativeHello("AOT") | Hello AOT! |
| A2 | =NativeSum(2, 3) | 5 |
Async functions and tasks
[ExcelAsyncFunction]
public static async Task<string> NativeAsyncTaskHello(string name, int msDelay)
{
await Task.Delay(msDelay);
return $"Hello native async task {name}";
}
[ExcelAsyncFunction]
public static string NativeAsyncHello(string name, int msToSleep)
{
Thread.Sleep(msToSleep);
return $"Hello native async {name}";
}
[ExcelFunction]
public static Task<string> NativeTaskHello(string name)
{
return Task.FromResult($"Hello native task {name}");
}
| Cell | Formula | Immediate Result | Final Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | =NativeAsyncTaskHello("Test", 5000) | #N/A | Hello native async task Test |
| B1 | =NativeAsyncHello("Test", 5000) | #N/A | Hello native async Test |
| C1 | =NativeTaskHello("Test") | Hello native task Test | Hello native task Test |
AddIn
public class AddIn : IExcelAddIn
{
public void AutoOpen()
{
var thisAddInName = Path.GetFileName((string)XlCall.Excel(XlCall.xlGetName));
var message = string.Format("Excel-DNA Native AOT Add-In '{0}' loaded!", thisAddInName);
MessageBox.Show(message, thisAddInName, MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
}
public void AutoClose()
{
}
}
Command
[ExcelCommand(MenuText = "MyNativeCommand")]
public static void NativeCommand()
{
MessageBox.Show("My NativeCommand");
}
Ribbon
public class RibbonController : IExcelRibbon
{
public string GetCustomUI(string RibbonID)
{
return @"
<customUI xmlns='http://schemas.microsoft.com/office/2006/01/customui'>
<ribbon>
<tabs>
<tab id='tab1' label='My Native Tab'>
<group id='group1' label='My Native Group'>
<button id='button1' tag='tagdata1' label='My Native Button1' onAction='OnButtonPressed1'/>
<button id='button2' tag='tagdata2' label='My Native Button2' onAction='OnButtonPressed2'/>
</group >
</tab>
</tabs>
</ribbon>
</customUI>";
}
public void OnButtonPressed1(RibbonControl control)
{
MessageBox.Show($"Hello1 from native control id={control.Id} tag={control.Tag}");
}
public void OnButtonPressed2(RibbonControl control)
{
MessageBox.Show($"Hello2 from native control id={control.Id} tag={control.Tag}");
}
}
DynamicApplication
To use the Excel COM object model from your command, function or ribbon handler, call ExcelDnaUtil.DynamicApplication. It returns an Excel.Application object as IDynamic, providing Get, Set, [] and Invoke methods:
[ExcelFunction]
public static string NativeApplicationName()
{
return (string)ExcelDnaUtil.DynamicApplication.Get("Name")!;
}
[ExcelFunction]
public static double NativeApplicationGetCellValue(string cell)
{
var workbook = (IDynamic)ExcelDnaUtil.DynamicApplication.Get("ActiveWorkbook")!;
var sheets = (IDynamic)workbook.Get("Sheets")!;
var sheet = (IDynamic)sheets[1]!;
var range = (IDynamic)sheet.Get("Range", [cell])!;
return (double)range.Get("Value")!;
}
[ExcelFunction]
public static double NativeApplicationGetCellValueT(string cell)
{
var workbook = ExcelDnaUtil.DynamicApplication.Get<IDynamic>("ActiveWorkbook");
var sheets = workbook.Get<IDynamic>("Sheets");
var sheet = (IDynamic)sheets[1]!;
var range = sheet.Get<IDynamic>("Range", [cell]);
return range.Get<double>("Value");
}
[ExcelFunction]
public static int NativeApplicationAlignCellRight(string cell)
{
var workbook = ExcelDnaUtil.DynamicApplication.Get<IDynamic>("ActiveWorkbook");
var sheets = workbook.Get<IDynamic>("Sheets");
var sheet = (IDynamic)sheets[1]!;
var range = sheet.Get<IDynamic>("Range", [cell]);
range.Set("HorizontalAlignment", -4152);
return range.Get<int>("HorizontalAlignment");
}
[ExcelFunction]
public static string NativeApplicationAddCellComment(string cell, string comment)
{
var workbook = ExcelDnaUtil.DynamicApplication.Get<IDynamic>("ActiveWorkbook");
var sheets = workbook.Get<IDynamic>("Sheets");
var sheet = (IDynamic)sheets[1]!;
var range = sheet.Get<IDynamic>("Range", [cell]);
var newComment = (IDynamic)range.Invoke("AddComment", [comment])!;
return newComment.Invoke<string>("Text", []);
}
| Cell | Formula | Result |
|---|---|---|
| C1 | 123.45 | |
| A1 | =NativeApplicationName() | Microsoft Excel |
| A2 | =NativeApplicationGetCellValue("C1") | 123.45 |
| A3 | =NativeApplicationGetCellValueT("C1") | 123.45 |
| A4 | =NativeApplicationAlignCellRight("C1") | -4152 |
| A5 | =NativeApplicationAddCellComment("C1", "My comment.") | My comment. |
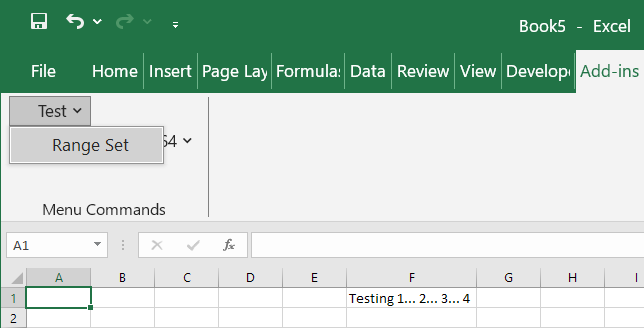
[ExcelCommand(MenuName = "Test", MenuText = "Range Set")]
public static void RangeSet()
{
IDynamic xlApp = ExcelDnaUtil.DynamicApplication;
xlApp.Get<IDynamic>("Range", ["F1"]).Set("Value", "Testing 1... 2... 3... 4");
}
IntelliSense
It is possible to get limited information regarding the UDF. The information can be seen by writing the name of the function in Excel's Forumla Bar and clicking on the fx button.
[ExcelFunction(Description = "A useful test function that adds two numbers, and returns the sum.")]
public static double AddThem(
[ExcelArgument(Name = "Augend", Description = "is the first number, to which will be added")]
double v1,
[ExcelArgument(Name = "Addend", Description = "is the second number that will be added")]
double v2)
{
return v1 + v2;
}
Accepting range parameters in UDFs
[ExcelFunction]
public static object NativeRangeConcat2(object[,] values)
{
string result = "";
int rows = values.GetLength(0);
int cols = values.GetLength(1);
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++)
{
object value = values[i, j];
result += value.ToString();
}
}
return result;
}
| Cell | Formula | Result |
|---|---|---|
| A1 | str | |
| A2 | 1 | |
| B1 | TRUE | |
| B2 | 3.5 | |
| C1 | =NativeRangeConcat2(A1:B2) | strTrue13.5 |
Extended Registration
Nullable parameter
[ExcelFunction]
public static string NativeNullableDouble(double? d)
{
return "Native Nullable VAL: " + (d.HasValue ? d : "NULL");
}
| Cell | Formula | Result |
|---|---|---|
| A1 | =NativeNullableDouble(1.2) | Native Nullable VAL: 1.2 |
| A2 | =NativeNullableDouble() | Native Nullable VAL: NULL |
Optional parameter
[ExcelFunction]
public static string NativeOptionalDouble(double d = 1.23)
{
return "Native Optional VAL: " + d.ToString();
}
| Cell | Formula | Result |
|---|---|---|
| A1 | =NativeOptionalDouble(2.3) | Native Optional VAL: 2.3 |
| A2 | =NativeOptionalDouble() | Native Optional VAL: 1.23 |
Range parameter
[ExcelFunction]
public static string NativeRangeAddress(IRange r)
{
return "Native Address: " + r.Get<string>("Address");
}
| Cell | Formula | Result |
|---|---|---|
| A1 | =NativeRangeAddress(B2) | Native Address: $B$2 |
| A2 | =NativeRangeAddress(B2:C4) | Native Address: $B$2:$C$4 |
| A3 | =NativeRangeAddress((B2,D5:E6)) | Native Address: $B$2,$D$5:$E$6 |
Enums parameter and return value
[ExcelFunction]
public static string NativeEnum(DateTimeKind e)
{
return "Native Enum VAL: " + e.ToString();
}
[ExcelFunction]
public static DateTimeKind NativeEnumReturn(string s)
{
return Enum.Parse<DateTimeKind>(s);
}
| Cell | Formula | Result |
|---|---|---|
| A1 | =NativeEnum("Unspecified") | Native Enum VAL: Unspecified |
| A2 | =NativeEnum("Local") | Native Enum VAL: Local |
| A3 | =NativeEnum(1) | Native Enum VAL: Utc |
| A4 | =NativeEnumReturn("Unspecified") | Unspecified |
| A5 | =NativeEnumReturn("Local") | Local |
String array parameter
[ExcelFunction]
public static string NativeStringArray(string[] s)
{
return "Native StringArray VALS: " + string.Concat(s);
}
| Cell | Formula | Result |
|---|---|---|
| A1 | 01 | |
| A2 | 2.30 | |
| A3 | World | |
| B1 | =NativeStringArray(A1:A3) | Native StringArray VALS: 12.3World |
String array 2D parameter
[ExcelFunction]
public static string NativeStringArray2D(string[,] s)
{
string result = "";
for (int i = 0; i < s.GetLength(0); i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < s.GetLength(1); j++)
{
result += s[i, j];
}
result += " ";
}
return $"Native StringArray2D VALS: {result}";
}
| Cell | Formula | Result |
|---|---|---|
| A1 | 01 | |
| A2 | 2.30 | |
| A3 | Hello | |
| B1 | 5 | |
| B2 | 6.7 | |
| B3 | World | |
| C1 | =NativeStringArray2D(A1:B3) | Native StringArray2D VALS: 15 2.36.7 HelloWorld |
params parameter (up to 16 arguments)
[ExcelFunction]
public static string NativeParamsFunc1(
[ExcelArgument(Name = "first.Input", Description = "is a useful start")]
object input,
[ExcelArgument(Description = "is another param start")]
string QtherInpEt,
[ExcelArgument(Name = "Value", Description = "gives the Rest")]
params object[] args)
{
return input + "," + QtherInpEt + ", : " + args.Length;
}
[ExcelFunction]
public static string NativeParamsFunc2(
[ExcelArgument(Name = "first.Input", Description = "is a useful start")]
object input,
[ExcelArgument(Name = "second.Input", Description = "is some more stuff")]
string input2,
[ExcelArgument(Description = "is another param ")]
string QtherInpEt,
[ExcelArgument(Name = "Value", Description = "gives the Rest")]
params object[] args)
{
var content = string.Join(",", args.Select(ValueType => ValueType.ToString()));
return input + "," + input2 + "," + QtherInpEt + ", " + $"[{args.Length}: {content}]";
}
[ExcelFunction]
public static string NativeParamsJoinString(string separator, params string[] values)
{
return String.Join(separator, values);
}
| Cell | Formula | Result |
|---|---|---|
| A1 | =NativeParamsFunc1(1,"2",4,5) | 1,2, : 2 |
| A2 | =NativeParamsFunc2("a",,"c","d",,"f") | a,,c, [3: d,ExcelDna.Integration.ExcelMissing,f] |
| A3 | =NativeParamsJoinString("//","5","4","3") | 5//4//3 |
Object handles
Create and reuse .NET objects:
public class Calc
{
private double d1, d2;
public Calc(double d1, double d2)
{
this.d1 = d1;
this.d2 = d2;
}
public double Sum()
{
return d1 + d2;
}
}
[ExcelFunction]
[return: ExcelHandle]
public static Calc NativeCreateCalc(double d1, double d2)
{
return new Calc(d1, d2);
}
[ExcelFunction]
public static double NativeCalcSum([ExcelHandle] Calc c)
{
return c.Sum();
}
| Cell | Formula | Result |
|---|---|---|
| A1 | =NativeCreateCalc(1.2, 3.4) | NativeCreateCalc:1 |
| A2 | =NativeCalcSum(A1) | 4.6 |
[ExcelHandle]
public class CalcExcelHandle
{
private double d1, d2;
public CalcExcelHandle(double d1, double d2)
{
this.d1 = d1;
this.d2 = d2;
}
public double Mul()
{
return d1 * d2;
}
}
[ExcelFunction]
public static CalcExcelHandle NativeCreateCalcExcelHandle(double d1, double d2)
{
return new CalcExcelHandle(d1, d2);
}
[ExcelFunction]
public static double NativeCalcExcelHandleMul(CalcExcelHandle c)
{
return c.Mul();
}
| Cell | Formula | Result |
|---|---|---|
| A1 | =NativeCreateCalcExcelHandle(1.4, 0.5) | NativeCreateCalcExcelHandle:1 |
| A2 | =NativeCalcExcelHandleMul(A1) | 0.7 |
[assembly: ExcelHandleExternal(typeof(System.Reflection.Assembly))]
[ExcelFunction]
public static System.Reflection.Assembly NativeGetExecutingAssembly()
{
return System.Reflection.Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly();
}
[ExcelFunction]
public static string? NativeGetAssemblyName(System.Reflection.Assembly assembly)
{
return assembly.GetName().Name;
}
| Cell | Formula | Result |
|---|---|---|
| A1 | =NativeGetExecutingAssembly() | NativeGetExecutingAssembly:1 |
| A2 | =NativeGetAssemblyName(A1) | ExcelDna.AddIn.RuntimeTestsAOT64 |
User defined parameter and return value conversions
public class TestType1
{
public string Value;
public TestType1(string value)
{
Value = value;
}
}
public class Conversions
{
[ExcelParameterConversion]
public static Version ToVersion(string s)
{
return new Version(s);
}
[ExcelReturnConversion]
public static string FromTestType1(TestType1 value)
{
return value.Value;
}
}
[ExcelFunction]
public static string NativeVersion2(Version v)
{
return "The Native Version value with field count 2 is " + v.ToString(2);
}
[ExcelFunction]
public static TestType1 NativeReturnTestType1(string s)
{
return new TestType1("The Native TestType1 return value is " + s);
}
| Cell | Formula | Result |
|---|---|---|
| A1 | =NativeVersion2("4.3.2.1") | The Native Version value with field count 2 is 4.3 |
| A2 | =NativeReturnTestType1("world") | The Native TestType1 return value is world |
Function execution handler
public class FunctionLoggingHandler : FunctionExecutionHandler
{
public override void OnSuccess(FunctionExecutionArgs args)
{
System.Diagnostics.Trace.WriteLine($"OnSuccess - Result: {args.ReturnValue}");
}
[ExcelFunctionExecutionHandlerSelector]
public static IFunctionExecutionHandler LoggingHandlerSelector(IExcelFunctionInfo functionInfo)
{
return new FunctionLoggingHandler();
}
}
| Cell | Formula | Result |
|---|---|---|
| A1 | =NativeHello("world") | Hello world! |
| DebugView | OnSuccess - Result: Hello world! |
Not supported functionality in native add-ins
Loading images for ribbon controls.
Copy to clipboard in Diagnostic Display.